《SpringBoot源码分析》CommandLineRunner
CommandLineRunner有什么用
在使用SpringBoot构建项目时,我们通常有一些预先数据的加载。那么SpringBoot提供了一个简单的方式来实现那就是CommandLineRunner。
什么是CommandLineRunner?
直奔主题:根据源码说明 我们可以通过实现CommandLineRunner接口并重写run方法来达到SpringBoot运行启动之后自动加载实现CommandLineRunner的类,同时我们可以定义多个类同时实现CommandLineRunner接口,通过@Order注解可以让它们排序执行,@Order()参数越小越先执行。
/**
* Interface used to indicate that a bean should <em>run</em> when it is contained within
* a {@link SpringApplication}. Multiple {@link CommandLineRunner} beans can be defined
* within the same application context and can be ordered using the {@link Ordered}
* interface or {@link Order @Order} annotation.
* <p>
* If you need access to {@link ApplicationArguments} instead of the raw String array
* consider using {@link ApplicationRunner}.
*
* @author Dave Syer
* @since 1.0.0
* @see ApplicationRunner
*/
@FunctionalInterface
public interface CommandLineRunner {
/**
* Callback used to run the bean.
* @param args incoming main method arguments
* @throws Exception on error
*/
void run(String... args) throws Exception;
}示例演示
需求:在启动SpringBoot之后,我们需要从数据库中预加载指定数据,并将输出信息按照指定顺序排序。(不要在意这个并不合理存在的例子)
实现:定义两个类分别实现CommandLineRunner并重写run方法,分别在run方法中处理业务逻辑即可。
/**
* @description: CommandLineRunner源码分析
* @Author MRyan
* @Date 2020/12/3 15:53
* @Version 1.0
*/
@SpringBootApplication
@Order(1)
@Slf4j
public class DataSourceBackup implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
showData();
}
public void showData() {
jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from user").forEach(row -> {
log.info("LOG1 " + row.toString());
});
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
@Order(2)
@Slf4j
class DataSourceBackup2 implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void run(String... args) {
showData();
}
public void showData() {
jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from TAG").forEach(row -> {
log.info("LOG2 " + row.toString());
});
}
}运行输出: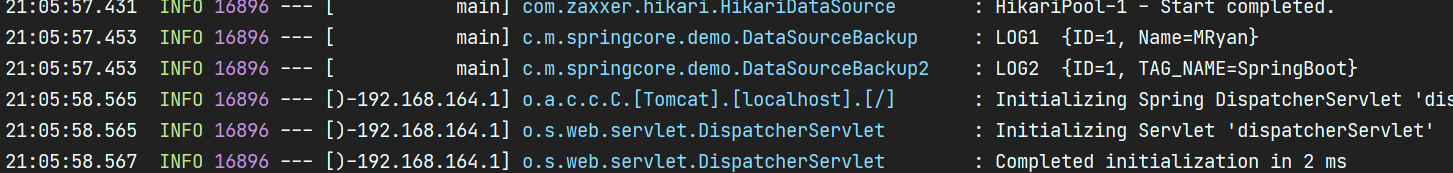
成功了,让我们来看看SpringBoot底层究竟是怎么实现的
源码分析
启动SpringBoot
(这块涉及到SpringBoot启动流程分析 之前分析过这里不再详述 可以看之前的文章)
《SpringBoot源码分析》启动流程
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}单点步步调试
执行run方法
定位到public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String… args)方法,开始分析吧
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 创建并启动计时监控类
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 声明应用上下文对象和异常报告集合
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
// 设置系统属性 headless 的值
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
// 创建所有 Spring 运行监听器并发布应用启动事件
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
// 处理 args 参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 创建 Banner 的打印类
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
// 创建应用上下文
context = this.createApplicationContext();
// 实例化异常报告器
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
// 准备应用上下文
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新应用上下文
this.refreshContext(context);
// 应用上下文刷新之后的事件的处理
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 停止计时监控类
stopWatch.stop();
// 输出日志记录执行主类名、时间信息
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 发布应用上下文启动完成事件
listeners.started(context);
// 执行所有 Runner 运行器
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
// 发布应用上下文就绪事件
listeners.running(context);
// 返回应用上下文对象
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
}其中关键步骤
// ************执行所有 Runner 运行器*********
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);进入callRunners方法内部
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
//将实现ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner接口的类,存储到集合中
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
//按照加载先后顺序排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}紧接着调用callRunner方法来处理各个实现类的逻辑
private void callRunner(CommandLineRunner runner, ApplicationArguments args) {
try {
//调用各个实现类中的逻辑实现
(runner).run(args.getSourceArgs());
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to execute CommandLineRunner", ex);
}
}
到这里关于CommandLineRunner部分的源码分析就到这里结束了,我们也了解了它的作用和实现原理应用场景了。